Identifying Natural Indicators of Water Sources
Recognising Vegetation as Water Indicators
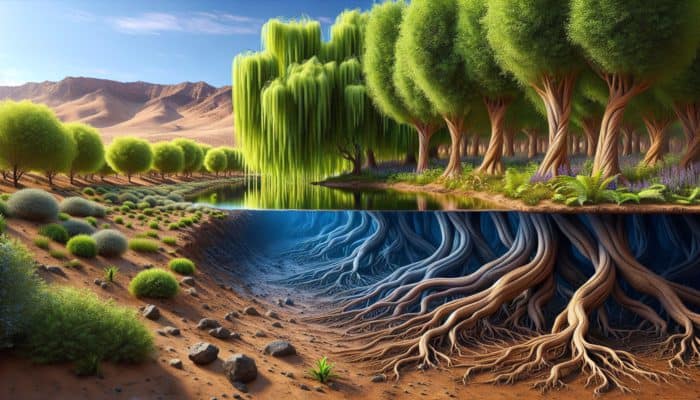

Finding Water in Nature: The presence of certain lush, green vegetation species is often a strong indicator of nearby water sources. In numerous ecosystems, specific plants such as willows, alders, and certain types of ferns flourish near water. These plants typically develop deep root systems that tap into underground aquifers or surface water, making their appearance a reliable sign of hydration potential. Observing the variety of foliage in your surroundings can help identify potential sources of water. For example, in arid regions like the Sahara Desert, the acacia tree is known to grow near groundwater, serving as a vital resource for both wildlife and human populations.
Moreover, various medicinal plants, especially those utilised in traditional medicine throughout the Amazon rainforest, typically grow in proximity to water. Their presence not only suggests accessible hydration but also indicates a rich biodiversity that thrives in these wet environments. The interdependence between flora and water sources is observable globally, from the vibrant wetlands of Florida to the lush valleys of the Himalayas, illustrating the essential role of water in sustaining life forms.
When exploring wilderness areas, it’s crucial to observe how vegetation changes in response to the landscape. Regions abundant in dense, thriving plant life often lead to streams, ponds, or underground water. By cultivating an awareness of the types of plants and their habitats, you can drastically enhance your ability to find water in nature successfully.
Interpreting Animal Behaviour for Water Clues
Animals possess an innate ability to locate water sources, often providing critical clues for individuals seeking hydration. For instance, you may notice that birds congregate near water, particularly in the early morning or late afternoon when they are most active. When watching wildlife, please pay attention to their movement patterns; animals often travel to water sources, creating trails that can lead you to hidden oases or watering holes.
In regions like Africa, elephants are known for digging into riverbeds to access underground water during dry seasons. Their behaviour not only reflects their intelligence but also points to potential water sources that may otherwise be overlooked. Similarly, in the Australian Outback, kangaroos and other wildlife seek refuge in dense thickets during the hottest parts of the day, returning to water sources at dawn and dusk.
Additionally, observing insect activity can provide insights into nearby water availability. For example, mosquitoes breed in stagnant water, while butterflies are often found around damp areas seeking hydration. Learning to interpret these behaviours enhances your ability to read the landscape and grasp the subtle cues of the ecosystem, significantly improving your chances of finding water.
Understanding Topographical Features as Water Indicators
A comprehensive understanding of the terrain is essential when searching for water in nature. Water naturally flows downhill, so valleys and land depressions serve as excellent starting points in your search. Pay attention to changes in elevation; lower areas often collect runoff and can lead to concealed streams or ponds. Valleys, ravines, and even the edges of cliffs can be strong indicators of nearby water sources.
In mountainous regions like the Rocky Mountains or the Andes, snowmelt generates streams that flow through valleys. The presence of lush vegetation on valley floors strongly signifies that water is nearby. Similarly, in coastal areas, the topographical layout can reveal hidden aquifers or springs that nourish adjacent wetlands. Understanding the relationship between landforms and water flow can significantly boost your likelihood of success in your quest for hydration.
Furthermore, unique geological formations, such as limestone karsts, often conceal underground rivers. By studying the landscape, one can identify potential locations where water may collect or flow, as is commonly seen in regions of Southeast Asia. This knowledge is vital for both outdoor enthusiasts and survivalists, providing a strategic approach to finding water in nature.
Examining Soil and Rock Formations for Water Clues
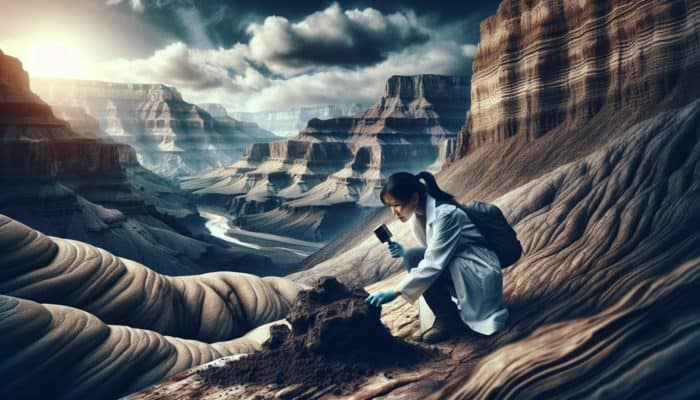

The type of soil and rock formations present can reveal substantial information regarding water availability. Moist, dark soil typically indicates that water lies close to the surface, while sandy or dry soils suggest that deeper digging may be necessary. Observing soil texture can guide your search; for instance, clay-rich soils tend to retain moisture, making them strong indicators of nearby water sources.
Rock formations can also provide critical clues. Water-carved rocks or smooth, rounded stones suggest the historical presence of flowing water. Many rivers and streams leave telltale signs on rocks, such as worn edges or polished surfaces, indicating that water has shaped the landscape over time. In locations like the Grand Canyon, these geological features narrate a tale of ancient water flow that can assist modern explorers.
Additionally, certain mineral deposits found within rock formations can indicate the presence of water. Areas rich in minerals, such as quartz, may lead to springs or aquifers. Exploring these geological features can unveil hidden treasures from nature, paving the way to finding water in the wilderness and ensuring survival.
Methods for Collecting Water in Nature
Effective Strategies for Digging for Water
When searching for water in arid regions, digging in dry riverbeds or low-lying areas can yield unexpectedly fruitful results. Underground water is often present beneath the surface, and its depth can vary based on soil type, seasonal changes, and environmental conditions. For instance, in sandy soils, water may only be a few feet below, whereas in clay soils, it may necessitate deeper excavation.
Adopting a systematic approach is crucial. Start by identifying potential sites near vegetation or animal trails, as these areas often correlate with water access. Once you have selected a site, you may use a shovel or even your hands to dig. If the soil is dry, it may require considerable effort to reach moisture, but patience frequently rewards the diligent seeker.
In deserts or arid landscapes, timing your digging is essential. During the hottest parts of the day, water may evaporate quickly, so attempting to dig during the cooler early morning or late afternoon hours can considerably enhance your chances. Additionally, if you encounter a pocket of water, having containers ready for collection is vital. This method of finding water in nature can be invaluable, especially when traditional sources are scarce.
Utilising Vegetation for Water Collection
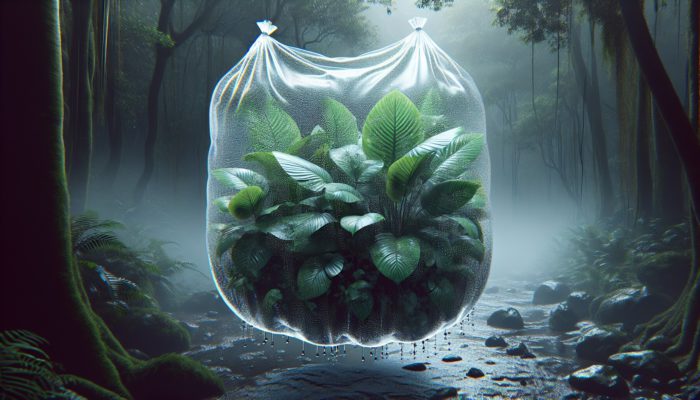

Leveraging the power of vegetation to collect water is both a sustainable and practical approach. A particularly effective method involves creating a transpiration bag. This technique entails enclosing leafy branches in clear plastic bags, allowing the natural process of transpiration to collect moisture. As plants release water vapour during photosynthesis, this vapour condenses on the inner surface of the bag, collecting as liquid water.
This method is especially effective in tropical and humid environments, where plant transpiration rates are markedly higher. For instance, in the Amazon rainforest, large-leafed plants can yield significant amounts of water, creating a natural reservoir for those in need. Moreover, this technique does not harm the plant; rather, it encourages awareness of sustainable practices.
Another method involves utilising large, succulent plants such as cacti. These plants store water within their tissues, and understanding how to access this resource can be a lifesaver. By carefully slicing open a cactus, one can access the moisture within, providing immediate hydration. However, caution is warranted, as some cacti contain toxins that can be harmful if ingested.
Overall, strategically employing vegetation can greatly enhance your ability to find water in the wild effectively. By grasping plant biology and leveraging natural processes, you can develop sustainable methods to ensure hydration while exploring diverse landscapes.
Constructing a Solar Still for Water Extraction
Building a solar still is an ingenious method to extract water from the ground or plant materials by harnessing the sun’s heat. This technique proves particularly beneficial in arid environments where traditional water sources may be limited. To construct a solar still, gather a few essential materials: a container for collecting water, a waterproof sheet, and a small rock.
Begin by digging a shallow hole and placing a container at the bottom of it. Next, cover the hole with the waterproof sheet, ensuring that it is airtight. Place a small rock in the centre of the sheet to create a dip, allowing condensation to gather and drip into the container below. As the sun heats the soil, moisture will evaporate and condense on the underside of the sheet, eventually dripping into the container.
This method can yield drinkable water, even in the driest conditions. Solar stills are effective because they harness the natural processes of evaporation and condensation, converting raw sunlight into a vital resource. Moreover, they require minimal resources, making them accessible for wilderness explorers and survivalists alike.
When using solar stills, it is essential to ensure that the collection container is clean to prevent potential contamination. The process may take several hours, so patience is essential. Understanding how to construct and effectively utilise a solar still broadens your toolkit for finding water in nature, emphasising innovation and sustainability.
Harvesting Rainwater for Sustainable Water Collection
Harvesting rainwater is one of the most efficient methods of collecting water, especially in areas that experience regular rainfall. Setting up a system for rain collection can significantly boost your chances of securing a sustainable water source. Begin by positioning clean containers, tarps, or gutters strategically to catch rainfall. The key is to ensure these items are free from contaminants, as dirty surfaces can compromise the quality of the collected water.
When rain falls, it can rapidly fill containers, especially during heavier showers. Across various cultures worldwide, rainwater harvesting has been a traditional practice integral to agricultural success. For instance, in India, rainwater is collected during the monsoon season and stored for use during the dry months, showcasing its importance as a sustainable resource.
Once collected, it is vital to store rainwater in sealed containers. Keeping it in a cool, dark place helps prevent bacterial growth and maintain water quality. Regularly checking for any signs of contamination or algae growth in stored water is also prudent.
Purifying rainwater is advisable, even though it is generally clean. Boiling or using chemical treatments can help ensure safety before consumption. The practice of rainwater harvesting not only aids in finding water in nature but also promotes sustainability, optimising natural resources for future use.
Collecting Dew as a Water Source
Collecting dew is a simple yet effective method for gathering water in humid environments. Dew forms overnight as temperatures drop, resulting in condensation that settles onto surfaces. To maximise your collection efforts, spread clean cloths or absorbent materials in open areas before sunset. The following morning, you can easily wring them out to collect fresh water.
This method proves particularly useful in regions with high humidity levels, such as tropical forests or coastal areas. The volume of water collected can be surprisingly substantial, especially when employing multiple cloths across various locations. In addition to clothes, using sponges or other absorbent materials can further enhance your water collection efforts, as they can soak up moisture directly from surfaces.
To effectively collect dew, timing is crucial. Early mornings, before the sun has fully risen, yield the best results, as this is when dew is most abundant. Understanding the patterns of dew formation allows for strategic collection, benefiting those on long hikes or outdoor adventures.
Dew collection not only provides essential hydration but also fosters an appreciation for the intricate ecosystems that produce this natural resource. By focusing on straightforward and eco-friendly methods, you can significantly enhance your ability to locate water in nature, even in seemingly dry conditions.
Purification Techniques for Collected Water
Utilising Boiling as a Reliable Water Purification Method
Boiling water remains one of the most dependable methods for purifying water, effectively killing pathogens, bacteria, and viruses. When collecting water in the wild, it’s crucial to ensure that any collected water is brought to a rolling boil for at least one minute. At higher elevations, where boiling points decrease, extending the boiling time to three minutes is recommended for thorough purification.
Boiling water is a straightforward process that requires minimal equipment; a portable stove or even a campfire can suffice. Using a metal container, such as a pot or canteen, facilitates effective heat transfer, ensuring the water reaches the necessary temperature. This method is advantageous because it doesn’t necessitate any special chemicals or equipment, making it accessible to anyone in the field.
However, boiling does not remove chemical contaminants or sediment. Therefore, pre-filtering water through cloth or sand can enhance the purification process, particularly in areas with visible debris. This two-step approach ensures that the water is not only safe to drink but also aesthetically pleasing.
In survival situations, having a fire-making kit and a metal container can be invaluable. Boiling water not only safeguards against illness but also instills confidence while navigating remote landscapes, emphasising the importance of robust purification techniques when finding water in nature.
Exploring Chemical Treatment for Water Purification
Chemical treatment represents another effective method for purifying water, particularly when boiling is not a viable option. Water purification tablets, often containing chlorine or iodine, are widely available and easy to use. Following the manufacturer’s instructions is crucial, as dosage and wait times can vary based on the specific product.
This method is particularly beneficial for backpackers and travellers who may lack access to boiling equipment. Simply adding the appropriate number of tablets to a designated amount of water allows for straightforward purification. While effective, it’s important to consider that some individuals may have sensitivities to iodine or chlorine; thus, having alternative methods or treatments could be beneficial in these situations.
In addition to tablets, liquid chemical treatments can also be used to disinfect water. It’s essential to ensure the water is clear before treatment, as turbidity can hinder the efficacy of the treatment. Pre-filtering the water can enhance the effectiveness of chemical treatments, making this a practical combination of methods to ensure the production of safe drinking water.
Understanding the various chemical treatment options available empowers individuals to make informed choices while finding water in nature. This enhances overall safety during outdoor adventures and emphasises the need for thorough preparation.
Leveraging Filtration Systems for Clean Water
Portable filtration systems have revolutionised how we purify water in the wilderness. These devices can effectively remove bacteria, protozoa, and sediment, ensuring that collected water is safe to drink. When selecting a filter, look for systems with a pore size of 0.2 microns or smaller, as this ensures the removal of most pathogens.
There are various types of filtration systems available, ranging from gravity-fed filters to hand-pump models. Gravity filters are particularly efficient, allowing water to pass through without requiring manual effort. They are ideal for camping and group trips, as they can purify larger quantities of water in a short amount of time.
When using a portable filter, it’s vital to adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions for maintenance and usage to ensure optimal performance. Regular cleaning and the replacement of filter cartridges can prevent contamination and maximise the lifespan of the device.
Furthermore, understanding the limitations of filtration systems is paramount. While effective against many pathogens, some filters may not be able to remove viruses. In such cases, combining filtration with chemical treatment can enhance safety and ensure that the water collected during your adventures is both safe and refreshing.
Investing in a high-quality filtration system can be a game-changer for outdoor enthusiasts, empowering them to confidently find water in nature while focusing on exploration and enjoyment.
Exploring Ultraviolet (UV) Light Purification for Water Safety
Ultraviolet (UV) light purification has emerged as a highly effective method for disinfecting water. UV light effectively kills bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens by altering their DNA, rendering them harmless. Portable UV purifiers are widely available and easy to use, making them an excellent choice for travellers and explorers.
To utilise a UV purifier, fill a container with water, insert the UV device, and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines. Depending on the model, the water may require exposure to UV light for several minutes to ensure effective purification. This method is particularly advantageous because it does not alter the water’s taste and does not require additional chemicals.
However, it’s essential to recognise that UV purification does not remove sediment or chemical contaminants. Therefore, pre-filtering water is advisable, especially in areas where water quality may be questionable.
Understanding how to harness the power of UV purification can significantly enhance your ability to find safe drinking water in various environments. This modern approach to water purification emphasises innovation and sustainability, aligning with contemporary practices in outdoor survival and exploration.
Harvesting Rainwater for Sustainable Water Supply
Strategies for Collecting Rainwater Effectively
Collecting rainwater is a sustainable and practical method for securing a water supply, particularly in regions with regular rainfall. Setting up a collection system requires careful planning to maximise the amount collected while ensuring cleanliness. Clean containers, tarps, or specially designed rainwater collection systems can significantly enhance your ability to gather this precious resource.
To begin, position containers in areas where rain commonly falls, ensuring they are free from contaminants. Tarps can be laid out to funnel rainwater into designated containers, while gutters can direct rainfall from rooftops into barrels. In many cultures, rainwater harvesting is a long-standing tradition, highlighting its effectiveness as a water source.
The beauty of rainwater lies in its purity, often requiring minimal treatment. However, it’s wise to treat collected rainwater before consumption, particularly if it has been stored for an extended period. Boiling or employing chemical treatments can eliminate any potential contaminants that might have settled in the storage container.
Understanding the significance of rainwater harvesting not only helps us find water in nature but also promotes a sustainable lifestyle. By embracing this practice, individuals can contribute to water conservation while preparing for dry spells or emergencies.
Best Practices for Storing Rainwater Safely
Proper storage of collected rainwater is crucial for maintaining its quality and safety. Using sealed, clean containers helps prevent contamination and keeps the water free from bacteria and algae. When selecting storage containers, look for those made from food-grade materials that are resistant to UV light, as this can degrade water quality over time.
Storing rainwater in a cool, dark place is essential to prevent bacterial growth. Regularly check the storage containers for signs of contamination or algae, and clean them as needed. This practice not only ensures safe drinking water but also prolongs the lifespan of your collected resource.
Implementing rainwater storage systems can enhance long-term water availability, particularly in areas with fluctuating rainfall patterns. Utilizing barrels, cisterns, or even underground tanks can optimise space and capacity for storing collected rainwater.
By prioritising proper storage methods, you’ll be well-equipped to handle various scenarios, ensuring that you have access to safe, fresh water whenever needed while adventuring or living in remote areas.
Purification Techniques for Collected Rainwater
While rainwater is often clean, purification methods are still recommended to ensure its safety. Boiling is one of the simplest and most effective methods, as it eliminates pathogens without requiring sophisticated equipment. Alternatively, chemical treatments can be used to disinfect the water, particularly when concerns about contaminants exist.
In addition to boiling and chemical treatments, filtration can also enhance the quality of rainwater. Portable filtration systems can remove sediments and improve taste, making the collected water more palatable. Combining these purification methods provides peace of mind, ensuring that the water is safe for drinking and cooking.
Understanding how to purify rainwater effectively is essential for maximising its potential as a sustainable water source. By developing a solid rainwater management strategy, you can confidently secure hydration while embracing eco-friendly practices in the great outdoors.
Collecting Dew and Frost for Water Retrieval
Utilising Cloth for Effective Dew Collection
Collecting dew using a cloth is a straightforward yet effective method for gathering water in humid environments. This method involves spreading clean cloths or absorbent materials across the ground overnight, allowing dew to settle on the fabric. Once the morning sun begins to rise, the dew can be easily collected by wringing out the cloth, yielding a refreshing source of moisture.
The amount of water collected can vary depending on environmental conditions; however, in areas with high humidity, this method can produce a surprisingly large quantity of water. Strategically placing cloths in open areas where dew forms most densely increases the chances of successful collection.
In addition to clothes, using absorbent materials like sponges can further enhance water collection efforts. These materials can absorb moisture directly from surrounding surfaces, providing an additional layer of resourcefulness in your quest to find water in nature.
Timing is crucial; collecting dew in the early morning before sun exposure maximises yield. By recognising the patterns of dew formation, you can effectively harness this natural resource, especially during outdoor excursions or camping trips.
Maximising Water Collection with Absorbent Materials
Utilising absorbent materials like sponges or chamois can optimise the collection of dew or frost from vegetation. By strategically placing these items on plants overnight, you can capture significant amounts of moisture. Once enough moisture is absorbed, squeeze the materials to extract the water, ensuring efficient collection.
This method is particularly effective during cooler months when frost forms on surfaces. The accumulation of frost can yield surprisingly large amounts of water when collected appropriately. Understanding the characteristics of local vegetation can enhance your success in using absorbent materials; some plants naturally retain more moisture than others.
Moreover, using absorbent materials can be a sustainable practice, as it fosters a connection with nature while ensuring hydration. This approach emphasizes the importance of resourcefulness and innovation, crucial attributes for anyone venturing into the wild.
Incorporating absorbent materials into your dew collection strategy can significantly enhance your ability to locate water in various environments, ultimately contributing to a successful outdoor experience.
Harnessing Early Morning Harvesting for Optimal Water Collection
The early morning hours present an ideal opportunity for collecting dew or frost directly from vegetation before it evaporates. This brief window allows for maximum water yield, making it an essential practice for outdoor enthusiasts. During this time, water is abundant on leaves, grasses, and various plants, just waiting to be captured.
To effectively harvest dew, approach vegetation quietly and use your hands or a cloth to collect moisture gently. In some cases, a container can be placed beneath the vegetation to gather dripping water as the sun rises. This technique emphasizes the importance of timing and situational awareness, thereby enhancing the chances of successful water collection.
In regions with high humidity, this early morning harvest can provide a crucial source of hydration, particularly for those on long hikes or camping trips. Harnessing the power of nature in this way strengthens the connection to the environment while showcasing the ingenious ways humans can adapt to their surroundings.
Understanding the patterns of dew formation and identifying the best times for collection can significantly improve your success in finding water in nature, ultimately enriching your outdoor experience.
Exploring Underground Water Sources
Identifying Aquifers and Their Significance
Spotting the signs of underground water sources is a vital skill for both survivalists and adventurers. Certain types of vegetation, particularly those that thrive in wet conditions, can indicate the presence of aquifers beneath the surface. Plants such as cattails and willows often grow near groundwater, suggesting that it may lie just below the surface.
Additionally, wet soil is a critical indicator. Areas with higher moisture content or periodic flooding may indicate access to underground water. Observing the topography can also provide insights into potential aquifer locations; valleys or depressions in the landscape often correlate with underground water flow.
Learning to identify these signs enhances your ability to effectively find water in nature, especially in environments where surface water is scarce. By developing a keen awareness of the landscape around you, you can significantly increase your chances of locating vital hydration sources hidden beneath the earth.
In various regions worldwide, aquifers serve as crucial lifelines for communities and wildlife. Understanding how to locate these resources empowers individuals to make informed decisions while navigating the wild.
Techniques for Digging Wells to Access Underground Water
Digging a well is a classic method for accessing underground water, enabling individuals to tap directly into aquifers. The success of this technique largely depends on the depth and geological composition of the local water table. In some areas, water may lie just a few feet below the surface, while in others, it may necessitate more extensive digging.
When digging a well, it’s essential to choose a location that shows signs of moisture or vegetation, as this can increase the likelihood of reaching water. Armed with a shovel and a bit of determination, individuals can often access groundwater, providing a reliable source of hydration.
However, digging a well is not without challenges. The process can be labour-intensive and may require multiple attempts to discover a viable water source. Moreover, ensuring that the well remains clean and protected from contamination is paramount, as unprotected wells can pose significant health risks.
Understanding how to dig a well equips survivalists and outdoor enthusiasts with a powerful tool in their quest to find water in nature. This technique showcases human resilience and resourcefulness in utilising natural resources for sustenance in challenging environments.
Utilising Natural Springs for Easy Water Access
Natural springs are a treasure trove for those seeking water, often providing a reliable source that requires minimal effort to access. Springs occur when groundwater flows to the surface, typically emerging in areas where geological formations create pressure points. Locating these springs can significantly enhance your ability to find water in nature.
To identify a natural spring, look for consistent moisture in the landscape, often accompanied by lush vegetation. The sound of trickling water or the sight of wet rocks can also serve as indicators. These springs are typically cold and refreshing, offering a delightful alternative to surface water sources.
While natural springs offer many benefits, it’s crucial to ensure that the water is safe for consumption. Testing or treating the water is advisable, as springs can become contaminated by surrounding wildlife or runoff. Understanding the characteristics of local springs can enrich your experience and enhance the reliability of these vital water sources.
Natural springs are invaluable resources for outdoor adventurers, highlighting the beauty of our ecosystems and their ability to provide for us. Embracing the discovery of these springs fosters a deeper connection to nature, enhancing the thrill of exploration.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the most effective natural indicators of water sources?
Look for lush vegetation, animal behaviour, topographical changes, and moist soil or rock formations to identify signs of nearby water sources.
How can I collect water using vegetation?
You can create transpiration bags around leafy branches to capture moisture from plants, or utilise large succulent plants, like cacti, to access stored water.
What are effective methods for purifying water in the wild?
Boiling, chemical treatments, filtration systems, and UV light purification are all effective techniques for ensuring water safety in outdoor settings.
What is a solar still, and how does it function?
A solar still is a device that utilises sunlight to evaporate water and condense it into a container, effectively purifying it in the process.
How can I successfully harvest rainwater?
Set up clean containers or tarps to catch rain, ensuring they are free from contaminants, and store the collected water properly in sealed containers.
What is the optimal time to collect dew for water?
Early in the morning, before the sun fully rises, is the best time to collect dew, as this is when moisture is most abundant on vegetation.
Is it possible to dig a well to access underground water?
Yes, digging a well can be an effective method for reaching underground water, but ensure you choose a location that shows signs of moisture or vegetation.
What are natural springs, and how can I locate them?
Natural springs occur when groundwater flows to the surface, often indicated by wet soil or lush vegetation. Listening for trickling water can also help locate them.
How do I purify collected rainwater?
While rainwater is often clean, it’s advisable to boil it or use chemical treatments to ensure safety before consumption.
What tools do I need to find water in nature?
Basic tools include a shovel for digging, cloth or absorbent materials for dew collection, and containers for storing and purifying water.
Explore our world on X!
Wildfire Defensible Space: Protecting Your Home
Crafting Effective Wildfire Defensible Space for Your Home What Is the Concept of Wildfire Defensible Space? Wildfire Defensible Space: A carefully managed, strategically designed area surrounding homes and properties designed to reduce the risk of fire damage significantly. This critical concept is essential for safeguarding structures, particularly in regions vulnerable to wildfires. Establishing defensible space is […]
Water Filter Comparisons: Your Ultimate Guide
Comprehensive Overview of Water Filter Types Understanding Reverse Osmosis Systems for Optimal Water Purity Water Filter Comparisons: Reverse osmosis (RO) systems are among the most sophisticated technologies available for water filtration. By employing a semipermeable membrane, these systems effectively eliminate a wide range of contaminants, including salts, heavy metals, and microorganisms. The filtration process involves […]
Water Collection Systems: Essential Solutions for Sustainability
Comprehensive Overview of Water Collection Systems What Exactly Are Water Collection Systems? Water Collection Systems: Water collection systems encompass a variety of innovative technologies and methodologies specifically developed to capture, store, and utilise water from diverse sources, with a primary focus on rainwater. These systems are crucial for the sustainable management of water resources, particularly in […]
Portable Water Filters: Essential for Clean Drinking
Comprehensive Guide to Portable Water Filters What Exactly Are Portable Water Filters? Portable Water Filters: Portable water filters are compact and efficient devices engineered to purify water from various sources, ensuring it is safe for consumption. These filters are essential tools for outdoor enthusiasts, travellers, and individuals preparing for emergencies. They provide access to clean […]







I find your exploration of vegetation as indicators of water sources truly captivating. It’s fascinating how interconnected ecosystems can be, and the knowledge of certain plants signaling water availability is not just useful for survival; it’s a remarkable testament to nature’s wisdom. I remember reading about indigenous tribes who have lived sustainably in arid regions for generations, relying on their deep understanding of local flora, like the acacia tree mentioned in your post. Their knowledge demonstrates a profound respect for nature and showcases the importance of traditional ecological wisdom.
Your reflection on indigenous knowledge and its connection to water sourcing resonates deeply. It’s inspiring to think about how communities have harmonized with their environments, weaving intricate tapestries of life that rely on nature’s cues. The acacia tree is just one example, but it’s fascinating how many plants can act as signposts in the landscape, guiding those who know their secrets.
I completely agree—traditional ecological wisdom truly exemplifies our relationship with nature. If you’re interested in exploring this topic further, I invite you to check out some insightful resources on how indigenous knowledge and local flora can guide sustainable practices.
https://survivalbite.com/LostFoods
This is a fascinating take on how we can read nature for clues about water sources. It’s interesting to think about how different cultures have relied on their understanding of vegetation for survival, particularly in harsh environments. In regions like the Amazon, as you mentioned, the connection between water and medicinal plants highlights the intricate balance of ecosystems and our dependency on them.
It’s fascinating to see how nature signals the presence of water through vegetation. I remember during a hike in a dry region, noticing clusters of willows near a stream—such a striking contrast to the surrounding dryness. It made me appreciate how in tune our ancestors were with their environment, relying on these natural indicators for survival.
Your exploration of vegetation as indicators of water sources really highlights the intelligence of nature in guiding us to vital resources. I’ve often noticed that in my own hiking adventures, particularly in more arid regions, the sudden emergence of lush greenery often signals nearby water, whether it be a river or underground springs.